Background
Isolated environment communication, such as between window.top and iframe; communication between environments in Chrome Extension; communication between the main thread and web worker; and so on. Native communication methods often encounter the following issues:
- Native communication methods do not support
response, for example:chrome.runtime.sendMessage(window | vscode | vscode.panel.webview |worker).postMessageElectron.WebContents.send
- Direct communication is not possible, forwarding is required:
- In
Chrome Extension, communication betweendevtooland the frontend page requires forwarding through acontent script.
- In
Each time this issue arises, I encapsulate a utility method that supports Promise. Since it happens often, I created a unified API library called bridge.
Usage
The usage process is similar to calling a backend API, as shown below:
The on method to listen for API
bridge.on(path: string, async function(params: any) {
const response = { ret: 0, data: 'Hello' }
return response
});
Explanation:
- path: API path, e.g., ‘web/getUserInfo’
- To differentiate between multiple environments, the path must start with the environment key
plat. - Unlike event listeners, one
pathcan only correspond to one method.
- To differentiate between multiple environments, the path must start with the environment key
- params: API parameters
- response: API return value
The request method to call an API
const response = await bridge.request(path, { username: 'yh' });
Explanation:
- path: Must be consistent with the
onpath
Example: chrome-extension Communication
Chrome Extension Environments
- web: frontend page
- content script
- popup
- devtool
- service worker: previously
background script

devtool or other environments need to communicate with web via forwarding through the content-script, as shown in the figure:
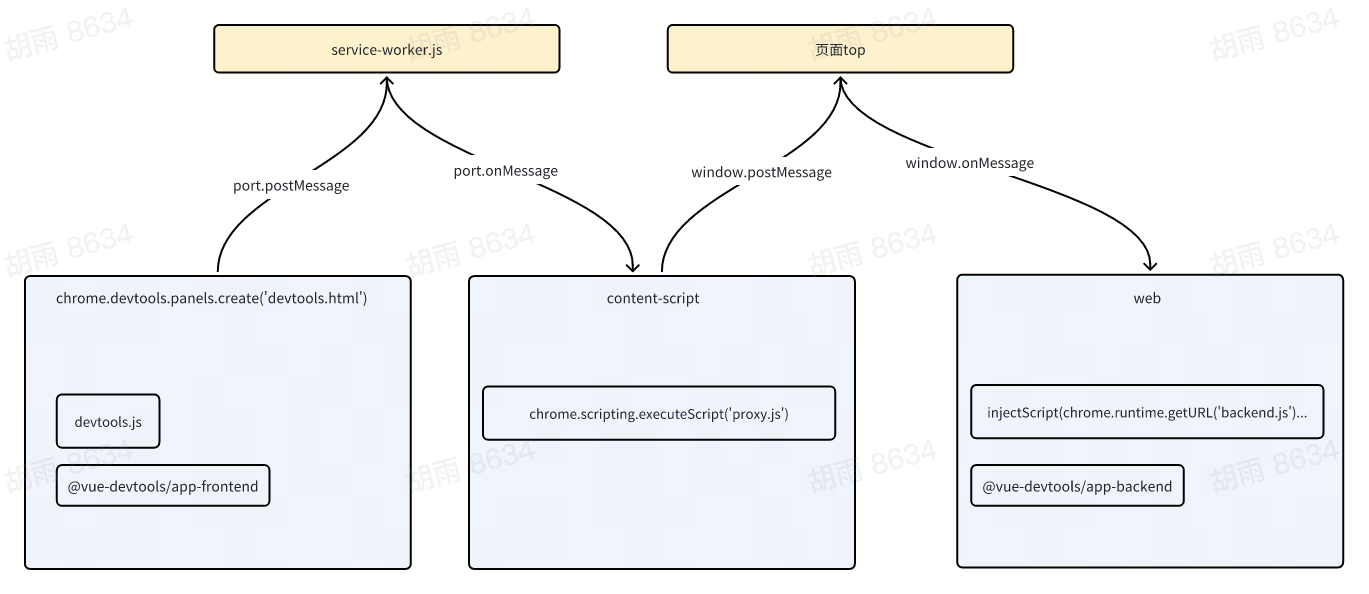
Chrome Extension using bridge
const Plat = {
web: 'testDevtoolsWeb'
};
const api = {
getPinia: `${Plat.web}/getPiniaInfo`
}
// content script
// must be required, if you want to request `web`
import { ContentBridge } from '@yuhufe/browser-bridge'
export const contentBridge = new ContentBridge({ platWeb: Plat.web })
// web.js
import { WebBridge } from '@yuhufe/browser-bridge'
export const webBridge = new WebBridge({ plat: Plat.web });
webBridge.on(api.getPinia, async function({ key }) {
console.log(key); // 'board'
return Promise.resolve({ a: 1 });
});
// devtool.js
import { DevtoolBridge } from '@yuhufe/browser-bridge'
export const devtoolBridge = new DevtoolBridge()
const piniaInfo = await devtoolBridge.request(api.getPinia, { key: 'board' });
console.log(piniaInfo); // { a: 1 }
Chrome Extension Bridges Introduction
WebBridge
- A single page may define multiple
WebBridges- Multiple
extensions extensionandiframecoexist
- Multiple
- To differentiate multiple
WebBridges, a customplatfield is required
ContentBridge
- Used to
proxycommunication between parties - Works with
WebBridge, requires defining theplatWebfield
DevtoolBridge
- Different Chrome Extensions’
devtools are isolated from each other, soplatdoes not need to be specified - The same applies to
popupandservice-worker
BackgroundBridge
PopupBridge
Example: iframe Communication
- top page: the host page
- Only one
- Uses
iframeEl.contentWindow.postMessageto communicate
- iframe page: the embedded page
- There may be multiple, so a
frameKeymust be specified - Uses
window.parent.postMessageto communicate
- There may be multiple, so a
const Plat = { frame1: 'iframeText', top: 'iframeTop' };
const api = {
getFrameInfo: `${Plat.frame1}/getInfo`,
getTopInfo: `${Plat.top}/getTopInfo`
}
// top.js
import { IFrameTopBridge } from '@yuhufe/browser-bridge'
const iframeTopBridge = new IFrameTop({
frameKey: Plat.frame1,
frameEl: document.querySelector('iframe')
})
iframeTopBridge.on(api.getTopInfo, async function({ topname }) {
console.log(topname);
return { top: 1 };
});
const userInfo = await iframeTopBridge.request(api.getFrameInfo, { username: '' });
// iframe.js
import { IFrameBridge } from '@yuhufe/browser-bridge'
const iframeBridge = new IFrameBridge({ frameKey })
// handle api
iframeBridge.on(api.getFrameInfo, async function({ username }) {
return { user: '', age: 0 }
});
// call api
const topInfo = await iframeBridge.request(api.getTopInfo, { topname: '' });
Example: WebWorker Communication
import { Plat } from '@yuhufe/browser-bridge'
const Plat = { worker1: 'worker1', master: 'master' }
const api = {
getWorkerInfo: `${Plat.worker1}/getInfo`,
getMasterInfo: `${Plat.master1}/getInfo`
}
// master.js
import { MasterBridge } from '@yuhufe/browser-bridge'
export const masterBridge = new MasterBridge()
const worker = new Worker(new URL('./worker.ts', import.meta.url), {
type: 'module',
})
masterBridge.bindWorker({ plat: Plat.worker, worker })
// handle api
masterBridge.on(api.getMasterInfo, async function () {
return { accessToken: 'aaa' }
})
// worker.js
import { WorkerBridge } from '@yuhufe/browser-bridge'
const workerBridge = new WorkerBridge()
const init = async function () {
const info: any = await workerBridge.request(api.getMasterInfo, null)
console.log(info)
}
init()
Custom bridge: Communication between two electron windows
The above only encapsulates common scenarios into bridge. You can also use BaseBridge to create custom encapsulations, as in the example below.
Communication parties: Two electron windows attached on global that need to communicate
- mainWin (
Electron.BrowserWindow) - backWin (
Electron.BrowserWindow)
Communication method
- Listen for events: use
ipcRenderer.onin their respective code- ipcRenderer comes from
Electron.IpcRenderer
- ipcRenderer comes from
- Trigger events:
backWincallsglobal.mainWin.webContents.send
Based on the above communication method, construct the bridge as follows:
import { BaseBridge, MsgDef } from '@yuhufe/browser-bridge'
const ipcRenderer = remote.ipcRenderer
export const WinPlat = {
backWin: 'backWin', // background window
mainWin: 'mainWin', // main window
}
export const WinAPI = {
backToggle: `${WinPlat.backWin}/toggle`,
cptDynamicUpdateFileInfo: `${WinPlat.backWin}/cpt-dynamicUpdate-fileInfo`,
ipclog: `${WinPlat.mainWin}/ipclog`,
}
export class ElectronBridge extends BaseBridge {
constructor({ plat }: any = {}) {
super({ plat })
this.init()
}
init() {
ipcRenderer?.on('kxBridgeMessage', (evt, message) => {
this.onReceiveMessage(message);
})
}
async sendMessage(message) {
const { target } = message
return global[target]?.webContents.send('kxBridgeMessage', message)
}
}
Explanation:
- Start listening for events during initialization
- Use
handleRequestto process request messages- Provide a specific implementation of
sendResponse, in this case directly forwarding
- Provide a specific implementation of
- Use
handleResponseto process response messages - Implement the
sendMessagemethod to send messages to otherbridges
ElectronBridge usage code is as follows:
// backWin
const backBridge = new ElectronBridge({ plat: WinPlat.backWin })
backBridge.on(WinAPI.cptDynamicUpdateFileInfo, async data => {
// business logic
return {}
})
// mainWin
const mainBridge = new ElectronBridge({ plat: WinPlat.mainWin })
const data = await mainBridge.request(WinAPI.cptDynamicUpdateFileInfo, {})
Custom bridge: Communication between vscode extension and tab page
The vscode extension opens a new tab page using a json file, and the tab page displays the graphical structure of the json.
Communication parties
vscode.extension: the execution environment of the vscode extension codepanel.webview: the execution environment of the vscode extension’s webviewjsonViewer: the actual json visualization page, page address (http://localhost:9999)
We want to establish a bridge between jsonViewer and vscode.extension, code is as follows:
export const EXTENSION_PLAT = {
vscode: 'vscode',
jsonViewer: 'jsonViewer',
}
// vscode.extension: send/receive messages via panel.webview
import { WebviewPanel } from 'vscode'
import { BaseBridge } from '@yuhufe/browser-bridge'
export class VSCodePanelBridge extends BaseBridge {
panel: WebviewPanel
constructor({ panel }: { panel: WebviewPanel }) {
super({ plat: EXTENSION_PLAT.vscode })
this.panel = panel
this.init()
}
init() {
this.panel.webview.onDidReceiveMessage(message => {
this.onReceiveMessage(message);
})
}
async sendMessage(message: any) {
await this.panel.webview.postMessage(message)
return
}
}
// panel.webview: only used for forwarding
window.addEventListener('message', event => {
if (event.data?.target === 'vscode') {
vscode.postMessage(event.data)
}
if (event.data?.target === 'jsonViewer') {
iframe.contentWindow.postMessage(event.data, '*')
}
})
// jsonViewer: inside an iframe, communication with panel.webview is the same as IFrameBridge
import { IFrameBridge } from '@yuhufe/browser-bridge'
export const vscodeWebBridge = new IFrameBridge({ frameKey: EXTENSION_PLAT.jsonViewer });
After that, communication between vscodeWebBridge and vscodePanelBridge works the same way as above.
Project Address
https://github.com/defghy/web-toolkits/tree/main/packages/wtool-chrome-bridge